Atomic structure and the periodic table worksheet – Unveiling the Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table: A Comprehensive Guide delves into the fundamental concepts of atomic structure and the organization of elements within the periodic table. This exploration unravels the mysteries of matter, providing a deeper understanding of the building blocks of our universe.
Delving into the subatomic realm, we uncover the intricacies of protons, neutrons, and electrons, their arrangement within atoms, and their influence on atomic properties. The periodic table emerges as a roadmap, guiding us through the periodic trends that govern the behavior of elements.
Introduction
Atomic structure is the fundamental building block of matter, understanding the arrangement and properties of subatomic particles within an atom. The periodic table, a tabular arrangement of chemical elements, organizes these elements based on their atomic structure and properties.
Atomic Structure
Subatomic Particles
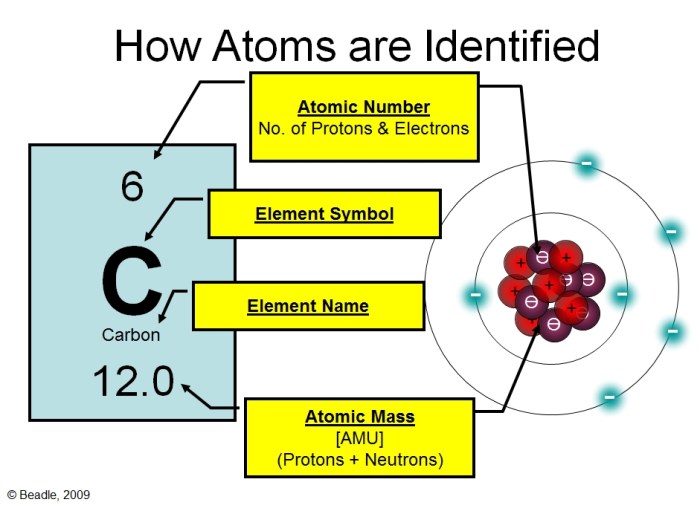
Atoms consist of three subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons reside in the nucleus, while electrons orbit around the nucleus in specific energy levels.
Atomic Number and Mass Number
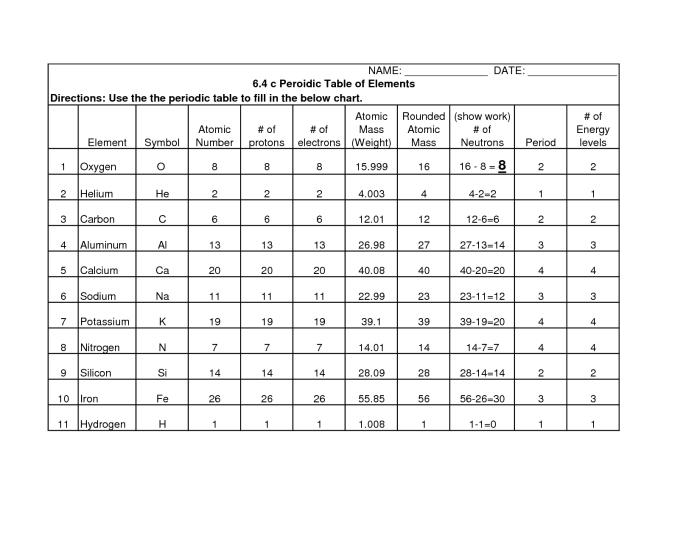
The atomic number, denoted by Z, represents the number of protons in an atom, which determines the element’s identity. The mass number, denoted by A, represents the total number of protons and neutrons in an atom.
Isotopes
Isotopes are atoms of the same element with the same atomic number but different mass numbers. They have the same chemical properties but differ in their neutron count.
Energy Levels and Electron Configurations, Atomic structure and the periodic table worksheet
Electrons occupy specific energy levels within an atom. The electron configuration describes the distribution of electrons in these energy levels, which influences the atom’s chemical properties.
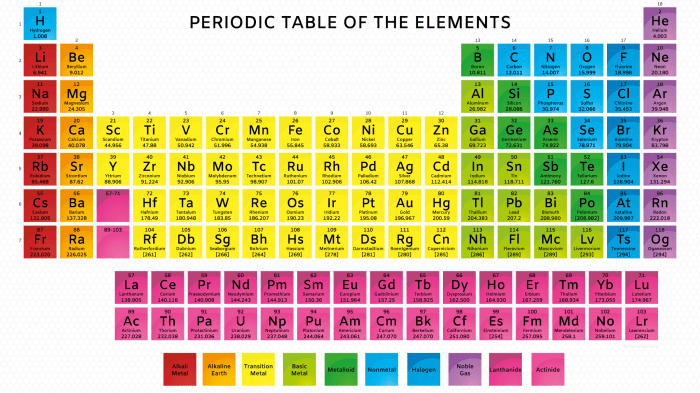
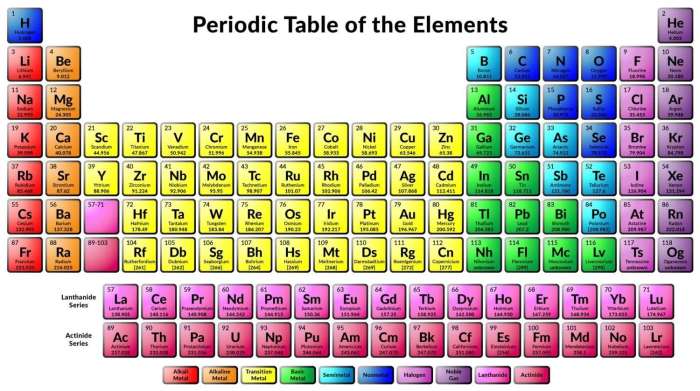
Periodic Table Organization
Vertical Groups and Horizontal Periods
The periodic table is organized into vertical groups (columns) and horizontal periods (rows). Elements in the same group share similar chemical properties due to their identical electron configurations in their outermost energy level.
Periodic Trends
Moving across a period from left to right, elements exhibit increasing atomic number, decreasing atomic radius, increasing ionization energy, and increasing electronegativity.
Element Groups
- Alkali Metals: Highly reactive metals with one valence electron.
- Halogens: Reactive nonmetals with seven valence electrons.
- Noble Gases: Inert gases with a stable electron configuration.
Using the Periodic Table: Atomic Structure And The Periodic Table Worksheet
Predicting Properties
The periodic table can be used to predict the properties of elements based on their position in the table. For example, elements in the same group tend to have similar chemical properties.
Chemical Reactions and Bonding
The periodic table helps explain chemical reactions and bonding. Elements with similar electron configurations tend to react in similar ways.
Limitations
While the periodic table is a valuable tool, it has limitations. It does not account for all exceptions or the complexities of chemical bonding.
Detailed FAQs
What is the significance of atomic structure?
Atomic structure determines the chemical properties and behavior of elements, shaping the interactions and reactions that occur in the world around us.
How does the periodic table organize elements?
The periodic table arranges elements based on their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties, providing a systematic framework for understanding their behavior.
What are the limitations of the periodic table?
While the periodic table is a powerful tool, it does not account for certain exceptions and complexities, such as the behavior of transition metals and the existence of isotopes.