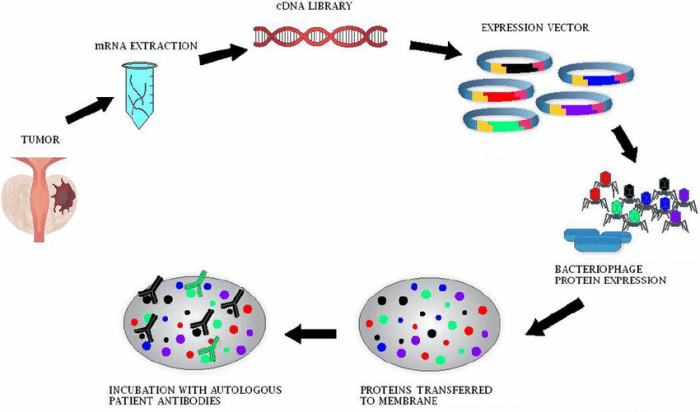
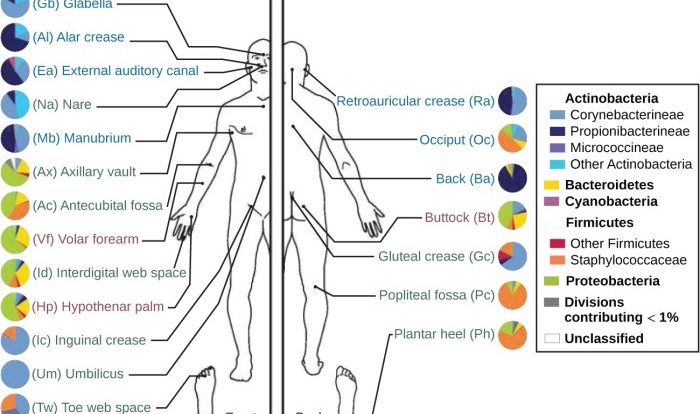
Serological analysis for bacterial identification typically involves using antigens and antibodies to identify and characterize different bacterial species. This technique plays a crucial role in clinical diagnostics, research, and the development of vaccines and treatments.
Serological techniques offer several advantages over other methods, including high specificity and sensitivity. However, they also have limitations, such as the need for specialized reagents and the potential for cross-reactivity.
Serological Analysis for Bacterial Identification: Serological Analysis For Bacterial Identification Typically Involves Using
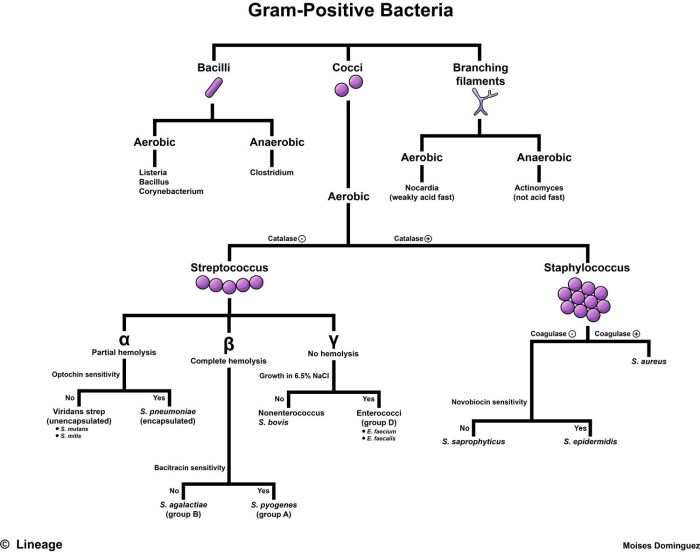
Serological techniques are valuable tools for bacterial identification, relying on the specific interactions between antigens and antibodies. These methods offer advantages in speed, sensitivity, and specificity, making them widely applicable in clinical diagnostics and research.
Antigens and Antibodies in Serological Analysis
Antigens are molecules recognized by the immune system as foreign or non-self. Antibodies are proteins produced by the immune system that specifically bind to antigens. In serological analysis, antibodies are used to target and identify different bacterial species based on the presence of specific antigens on their surfaces.
Common Serological Techniques
- Agglutination tests: Involve the cross-linking of antigens on bacterial cells by specific antibodies, leading to visible clumping or agglutination.
- Precipitation tests: Detect the formation of insoluble precipitates when antibodies bind to soluble antigens present in bacterial extracts.
- Immunofluorescence assays: Utilize fluorescently labeled antibodies to visualize the presence of specific antigens on bacterial cells or tissues.
Applications in Clinical and Research Settings, Serological analysis for bacterial identification typically involves using
Serological analysis is widely used in clinical diagnostics for:
- Identifying infectious agents responsible for diseases like pneumonia, meningitis, and bloodstream infections.
- Studying bacterial epidemiology to track the spread and evolution of bacterial pathogens.
In research, serological techniques contribute to:
- Developing vaccines and treatments by characterizing bacterial antigens and identifying targets for immune responses.
Advancements and Future Directions
Advancements in serological techniques include the development of:
- Multiplex assays: Allow simultaneous detection of multiple bacterial antigens, enhancing efficiency and accuracy.
- Biosensors: Utilize antibodies immobilized on surfaces to detect bacterial antigens in real-time, offering rapid and sensitive diagnostics.
Future research will focus on further improving sensitivity, specificity, and automation of serological techniques, as well as exploring their applications in point-of-care diagnostics and personalized medicine.
Common Queries
What are the advantages of using serological analysis for bacterial identification?
Serological analysis offers high specificity and sensitivity, allowing for accurate identification of bacterial species.
What are the limitations of serological analysis?
Serological analysis requires specialized reagents and can be time-consuming. Additionally, cross-reactivity can occur, leading to false-positive results.
What are the applications of serological analysis in clinical settings?
Serological analysis is used to identify infectious agents, study bacterial epidemiology, and develop vaccines and treatments.