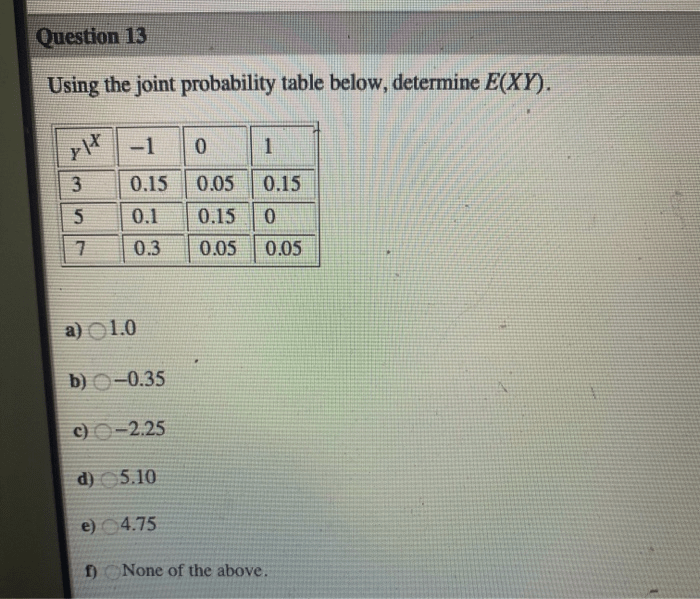
Using the joint probability table below determine e xy, we delve into the fascinating realm of probability theory. Joint probability tables serve as powerful tools for analyzing the interconnectedness of random variables, providing a structured framework for understanding their combined behavior.
This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and techniques necessary to navigate the intricacies of joint probability tables, empowering you to calculate E(XY) with precision and uncover valuable insights from data.
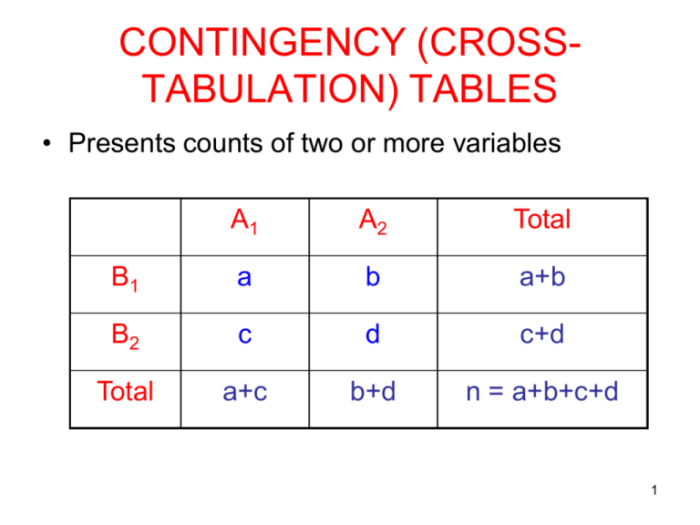
Joint Probability Tables
A joint probability table is a tabular representation of the joint probabilities of two or more random variables. It provides a complete description of the distribution of the random variables and allows for the calculation of probabilities and expected values.
Interpreting Joint Probability Tables, Using the joint probability table below determine e xy
Each cell in a joint probability table represents the probability of a specific combination of values for the random variables. The values in the table sum to 1, representing the total probability of all possible outcomes.
For example, consider a joint probability table for the random variables X and Y:
| Y | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| X | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.1 |
| 2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
This table shows that the probability of X = 1 and Y = 2 is 0.2, and the probability of X = 2 and Y = 3 is 0.2.
Calculating E(XY) using Joint Probability Tables
The expected value of the product of two random variables, E(XY), can be calculated using a joint probability table as follows:
- Multiply each cell in the table by the corresponding values of X and Y.
- Sum the resulting values to obtain E(XY).
For example, using the joint probability table above, we have:
- (1 x 1 x 0.2) + (1 x 2 x 0.3) + (1 x 3 x 0.1) + (2 x 1 x 0.1) + (2 x 2 x 0.2) + (2 x 3 x 0.2) = 1.6
Therefore, E(XY) = 1.6.
Applications of E(XY)
E(XY) is a useful statistic in various fields, including:
- Statistics:Measuring the correlation between two random variables.
- Finance:Calculating the expected return of an investment portfolio.
- Engineering:Estimating the reliability of a system.
FAQ Overview: Using The Joint Probability Table Below Determine E Xy
What is the purpose of a joint probability table?
A joint probability table provides a comprehensive representation of the probabilities associated with the outcomes of multiple random variables.
How do I calculate E(XY) using a joint probability table?
To calculate E(XY), multiply each cell value in the joint probability table by the product of the corresponding X and Y values, then sum the results.
What are the applications of E(XY) in real-world scenarios?
E(XY) finds applications in fields such as finance, engineering, and decision-making, where it helps quantify the expected value of the product of two random variables.