Art Labeling Activity Components of Blood: An in-depth exploration of the vital processes and techniques involved in labeling blood components, ensuring accurate identification and safe transfusions.
This comprehensive guide delves into the significance of labeling blood components, examining the methods employed and emphasizing the crucial role of precision and consistency in labeling practices.
Labeling Blood Components: Art Labeling Activity Components Of Blood
Labeling blood components is a critical process that ensures the safety and efficacy of blood transfusions. It involves identifying and marking blood products with accurate information about their contents, compatibility, and intended use.
The primary purpose of labeling blood components is to prevent errors and ensure that the right blood product is transfused into the correct patient. It also facilitates inventory management, traceability, and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Methods of Labeling Blood Components
- Manual Labeling:Blood components are manually labeled by trained personnel using adhesive labels or tags.
- Automated Labeling:Automated labeling systems use barcode scanners and software to generate and apply labels directly to blood components.
- Electronic Labeling:Electronic labeling systems use electronic devices to store and display information about blood components, eliminating the need for physical labels.
Regardless of the method used, accurate and consistent labeling is essential to ensure the safety of blood transfusions.
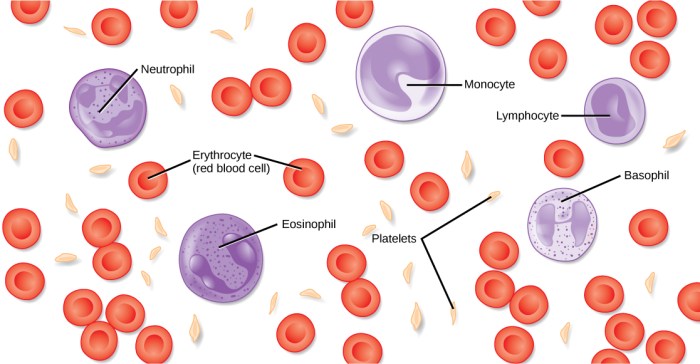
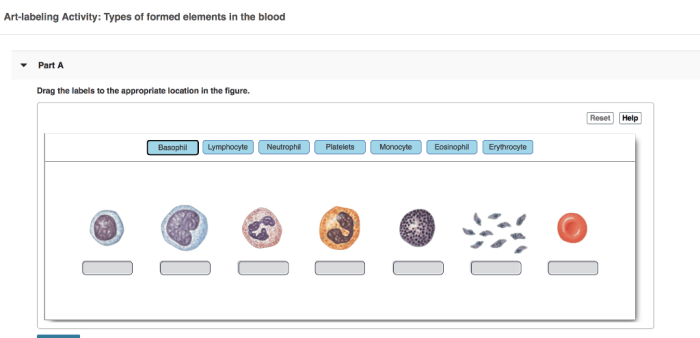
Components of Blood
Blood is a complex fluid that consists of several major components:
Plasma
- Liquid component that makes up about 55% of blood volume.
- Contains proteins (e.g., albumin, globulins), electrolytes, nutrients, and waste products.
Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
- Contain hemoglobin, which carries oxygen to tissues.
- Make up about 45% of blood volume.
White Blood Cells (Leukocytes)
- Part of the immune system, fighting infections.
- Make up less than 1% of blood volume.
Platelets (Thrombocytes)
- Aid in blood clotting.
- Make up less than 1% of blood volume.
These components work together to maintain blood volume, transport nutrients and oxygen, fight infections, and prevent excessive bleeding.
Blood Typing
Blood typing is a process of determining the presence or absence of specific antigens on the surface of red blood cells. These antigens, known as the ABO and Rh systems, play a crucial role in determining blood compatibility for transfusions.
ABO Blood Types
- Type A: Has A antigen.
- Type B: Has B antigen.
- Type AB: Has both A and B antigens.
- Type O: Has neither A nor B antigen.
Rh Factor
- Rh-positive: Has the Rh antigen.
- Rh-negative: Lacks the Rh antigen.
Compatibility for blood transfusions requires matching the ABO and Rh types of the donor and recipient.
Transfusion Medicine
Transfusion medicine involves the administration of blood components to patients for various medical reasons, such as blood loss, anemia, or immune disorders.
Indications for Blood Transfusion
- Severe blood loss (e.g., trauma, surgery).
- Anemia (low red blood cell count).
- Immune disorders (e.g., hemophilia, leukemia).
Contraindications for Blood Transfusion, Art labeling activity components of blood
- Incompatible blood type.
- Active infection.
- History of allergic reactions to blood products.
Risks and Benefits of Blood Transfusion
Blood transfusions carry both risks and benefits, including:
- Risks:Infection, allergic reactions, transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI).
- Benefits:Restores blood volume, improves oxygen delivery, corrects coagulation disorders.
Quality Control
Quality control is paramount in blood labeling and transfusion to ensure the safety and effectiveness of blood products.
Quality Control Measures
- Donor screening:Assessing donors for infections, health conditions, and blood compatibility.
- Blood component testing:Performing laboratory tests to confirm blood type, screen for infections, and ensure product quality.
- Labeling verification:Verifying the accuracy and consistency of blood component labeling.
- Inventory management:Tracking blood components, ensuring proper storage and timely distribution.
These measures help minimize errors, maintain product integrity, and enhance patient safety.
General Inquiries
What is the purpose of labeling blood components?
Labeling blood components ensures accurate identification, tracking, and proper handling throughout the transfusion process, minimizing errors and safeguarding patient safety.
What are the different methods used for labeling blood components?
Blood components can be labeled manually or through automated systems, utilizing various techniques such as barcoding, RFID tags, and electronic labeling.
Why is accurate and consistent labeling of blood components important?
Accurate labeling is crucial for preventing transfusion errors, ensuring compatibility between donor and recipient blood, and facilitating effective inventory management.